SRM样品管理标准化
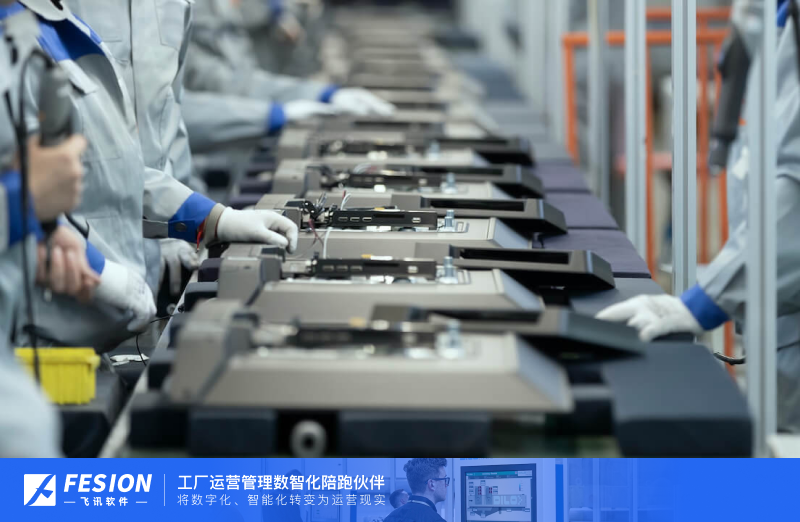

SMP Standardization: Advancing Sample Management
Introduction
In the realm of scientific research, the efficient management of samples plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate and reliable results. The advent of SRM (Sample Resource Management) has revolutionized the way samples are handled, stored, tracked, and shared. This article explores the significance of SRM and the benefits it offers in standardizing sample management practices.
What is SRM?
SRM, or Sample Resource Management, refers to a comprehensive system of protocols and procedures designed to streamline and standardize the management of research samples. It encompasses various stages of the sample lifecycle, including collection, labeling, storage, retrieval, tracking, and disposal. The aim of SRM is to ensure the integrity, traceability, and accessibility of samples, thereby enhancing research efficiency and reproducibility.
The Need for Standardization
Prior to the establishment of SRM, sample management practices varied significantly across laboratories and research institutions. This lack of standardization often resulted in inefficiencies, errors, and challenges in reproducing research findings. By implementing SRM, organizations can minimize these issues and create a unified approach to sample management.
Key Components of SRM
1. Sample Identification and Labeling
An essential aspect of SRM is the proper identification and labeling of samples. Each sample should have a unique identifier that allows for easy tracking and retrieval. Barcoding or RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tagging can be used to automate this process and minimize human error.
2. Storage Infrastructure
SRM emphasizes the importance of using specialized storage infrastructure for samples. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure can significantly impact sample stability. Therefore, dedicated storage facilities equipped with appropriate temperature-controlled units are essential to maintain sample integrity.
3. Database and Tracking Systems
Implementing a robust database and tracking system is crucial for effective SRM. These systems enable researchers to record detailed information about each sample, including its origin, processing history, and location. This centralized database streamlines sample tracking, retrieval, and sharing, while also ensuring data security.
4. Training and Quality Control
SRM necessitates comprehensive training programs to ensure that all personnel involved in sample management adhere to standardized protocols. Regular quality control measures, such as proficiency testing and internal audits, should also be implemented to identify and rectify any deviations from established procedures.
The Benefits of SRM
1. Improved Research Efficiency
By implementing SRM practices, research organizations can optimize their workflow and enhance efficiency. Standardized procedures minimize the time spent on sample handling, tracking, and retrieval, allowing scientists to focus more on actual research activities.
2. Enhanced Data Quality and Reproducibility
SRM ensures the integrity and traceability of samples, reducing the risk of errors that could compromise research findings. Standardized practices improve data quality and facilitate the reproducibility of experiments, contributing to the overall reliability of scientific research.
3. Facilitated Collaboration and Sharing
SRM promotes seamless collaboration and sample sharing between research institutions. With standardized protocols and a centralized database, scientists can easily locate and request specific samples, fostering scientific advancements through improved knowledge exchange.
4. Cost Savings
Efficient sample management through SRM can result in cost savings for research organizations. By minimizing sample loss, duplication, and errors, valuable resources are preserved. Moreover, optimizing storage and retrieval processes prevents unnecessary expenses associated with mishandled or misplaced samples.
Conclusion
SRM has emerged as a game-changer in the field of sample management, offering a standardized approach that improves research efficiency, data quality, collaboration, and cost-effectiveness. By implementing SRM practices, research organizations can unlock the full potential of their scientific endeavors and pave the way for groundbreaking discoveries.
Remember, to develop successful research outcomes, it is vital to implement efficient and standardized sample management practices. Embracing SRM ensures that research institutions stay at the forefront of scientific advancements while upholding data integrity and reproducibility.
��Ѷ���������2006�꣬ӵ�������з����뿪��ƽ̨����һ�Ҽ���Ӫ�������졢�ɹ���ȫ��·���ǻ��������Ʒ����̺ͷ����̡���Ʒ�������ֻ����䡢����������������������˾��MRO��ERP��MES��WMS��CRM��SRM�Ȳ�ƷΪ������Ϊ�ͻ��ṩ���ǻ��������巽���滮��������ܷ�����Χ���������Ǻͳ����ǵ����������ڰ����ͻ������к�ʵ�ʳ������ɴ��С��ɴ��µ����ֻ���Ӫ��ϵ�������������Ϣ�����������ֻ��;������ܻ��������⣬Ϊ��ͬ��ҵ����ͬ��ʵ�ֲ�ͬ�ľ�ӪĿ�ꡣ






















请先 登录后发表评论 ~